## Brilliant Quantum Computing Course [(link)](https://brilliant.org/courses/quantum-computing/)
Comment:
- Good starting material especially when you have classic computer algorithm knowledge.
- Only 2 classes (including reviewing) per day for free.
My Take aways (some basic concepts won't be covered):
- Information Thoery:
- can be used to determined/calculate the minimal steps to answer a question.
- n-bits: represent 1 state at a time (total 2^n)
- n-qubits: represent 2^n states at a time.
- Superdense: use both X axis and Z axis to encode 2 information
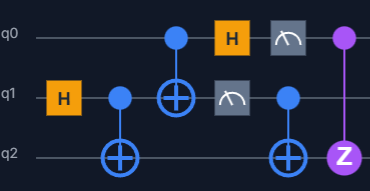
- Quantum teleportation:
- encode information on 2 axis (with an ancilla qubit) and apply the gates based on measurement:
- Oracle:
- needs to be irreventable, Schrödinger equation
- $U \ket{x0} = \ket{x}\ket{f(x)}$
- $U \ket{x1} = \ket{x}\ket{1 \oplus f(x)}$
- Orthogonal:
- If two states are not orthogonal, then there is a overlapped area with non-zero probability.
- i.e. $ \braket{\phi|\psi}$ won't be 0
- Questions
- Deutsch question
- Q: tell whether a funciton is balanced or constant
- A: Construct $|00..0>$ in a way that it will become different when a function is balanced/constant
- BV question
- Q: $f(x) = a\cdot x (mod 2)$ , try get $a$ when only $f(x)$ is given.
- A:
- variant: counterfiet coins Redux question
- QC in reality, difficulties:
- maintain state for long-term
- high fedility gates
- Q simulated annealing:
- example questions: spin system, knapsack problem
- local mins are global min in QSA.
- there is no entanglement